Bloodhound: Using Databases
Legacy Documentation
You're viewing legacy documentation for API Fortress (deployed via an on-premises container). To view documentation for the new SaaS version of API Fortress — now known as Sauce Labs API Testing and Monitoring (with Sauce Connect tunnels) — see API Testing on the Sauce Labs Cloud.
In the following walkthrough we’ll show you how to use Bloodhound to turn a database into a data API. In this example, we will use the Bloodhound Template found on Github and use Postgres as the database. The template will deploy a Postgres database to experiment with, but you will obviously want to connect it to your database once you understand the mechanics.
-
First, we deploy the entire package found in the templates folder. This will deploy Bloodhound as well as the databases.
sudo docker-compose up -d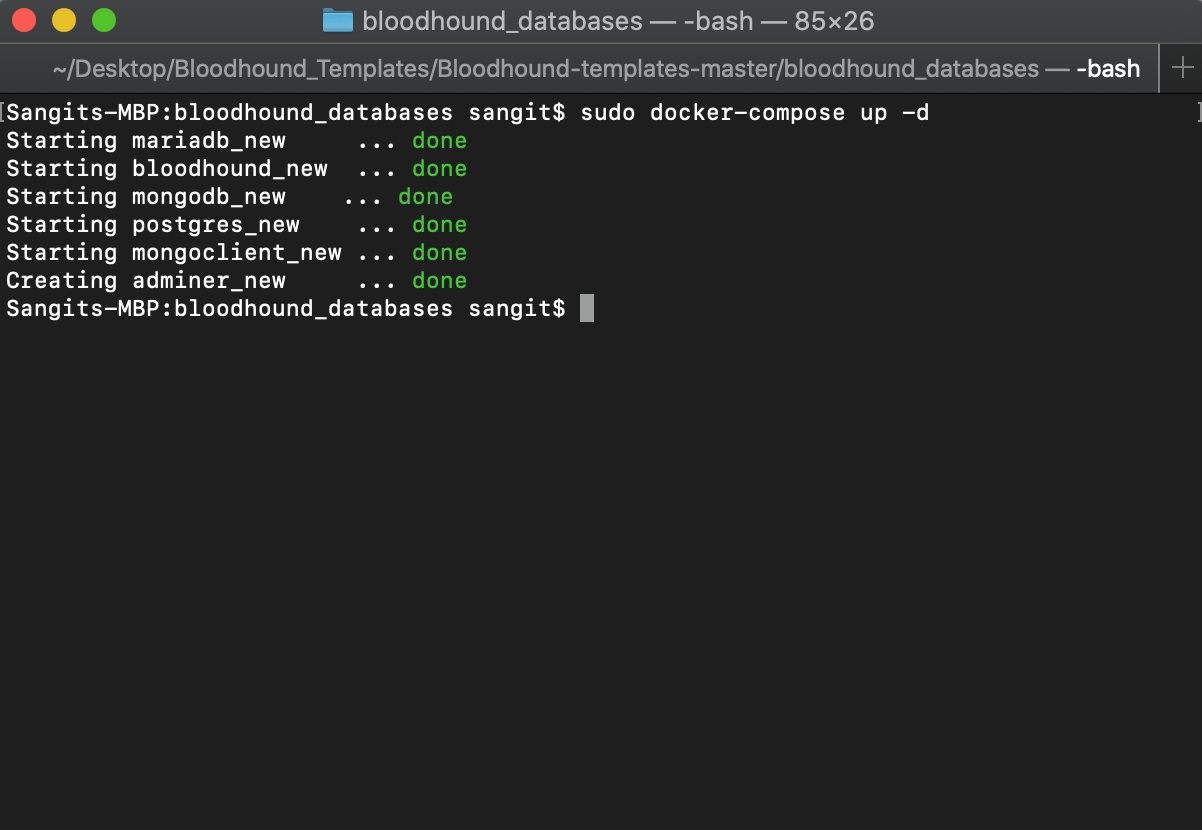
-
Next, to allow you to experiment with our demo setup, we will point our browser to “http://localhost:8081” and use the following settings:
System: PostgreSQL
Server: postgres
Username: apipulse
Password: jk5112
Database: apipulse
And load the test data in the UI.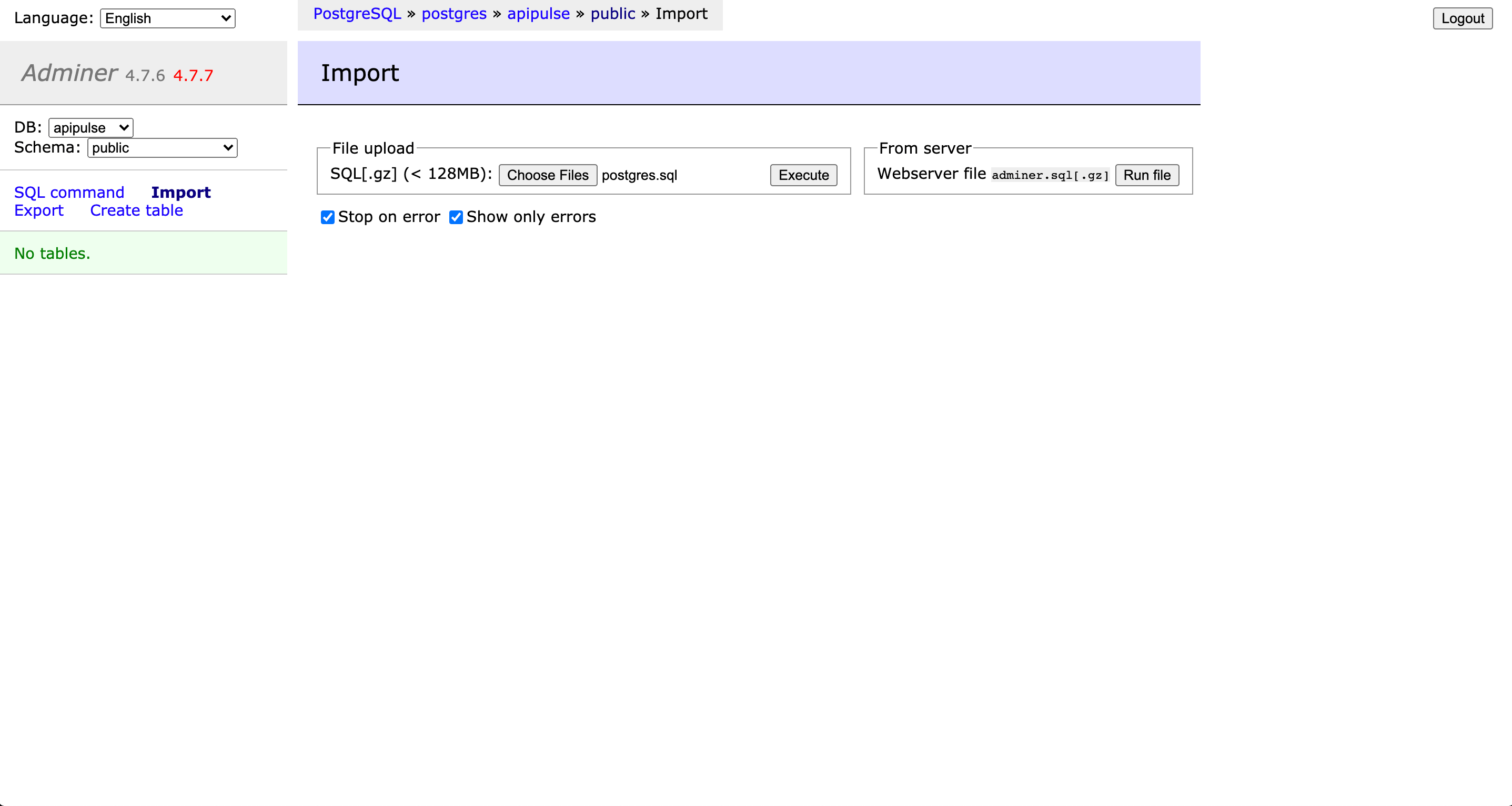
To do this we will click on “Import” and load the “postgres.sql” file and click on “Execute” (NOTE: This will throw an error but it has no effect)
-
Now that we have our database populated with test data, we can query it using the API “localhost:8080/postgres.” Let’s try a “select” query. We will execute the following curl command “curl -H 'content-type:text/plain' -d 'select * from orders' localhost:8080/postgres“
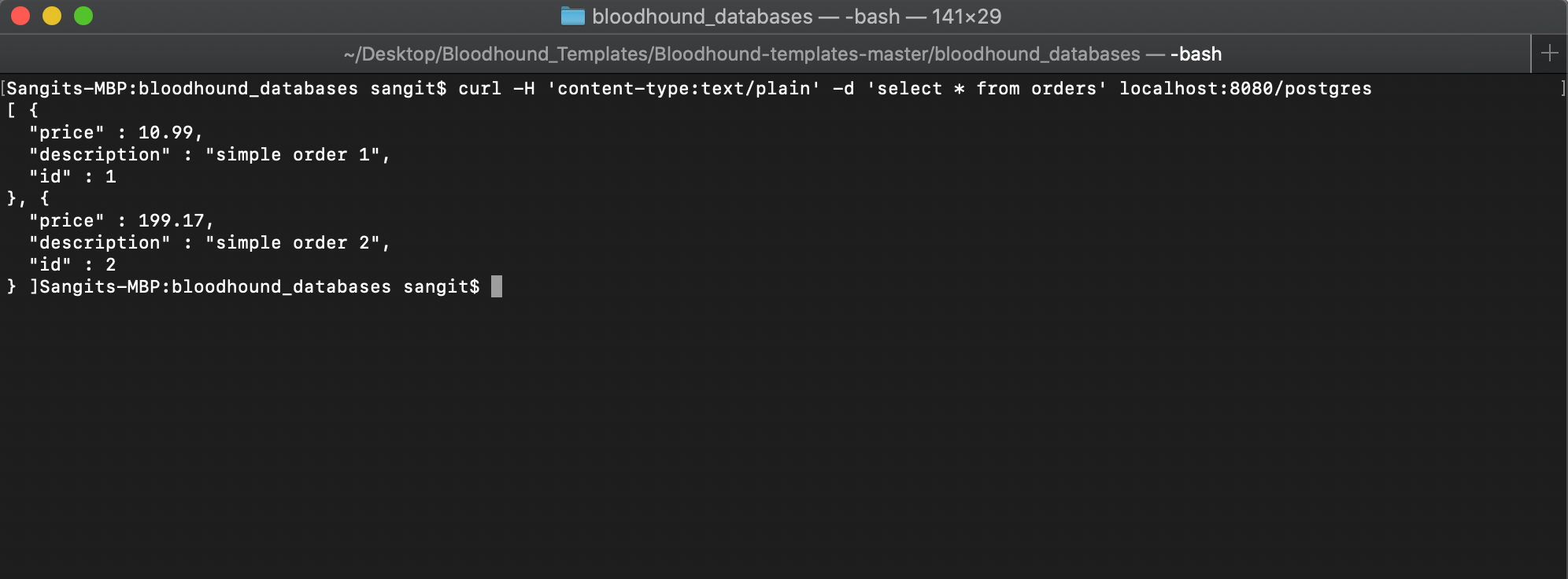
-
All of the other query operations are also supported via the API call localhost:8080/postgres, which can be the first step in your data-driven multi
-
-step API test. Use this API in your automated API testing suite.
-
As mentioned in the beginning, once you understand the mechanics you can configure the module to connect to your jdbc databases by modifying the flow yaml. You can learn more about the module and it’s configurations here.
-
Visit the Bloodhound Wiki to learn about configuration options.