Jenkins: Using the API
Legacy Documentation
You're viewing legacy documentation for API Fortress (deployed via an on-premises container). To view documentation for the new SaaS version of API Fortress — now known as Sauce Labs API Testing and Monitoring (with Sauce Connect tunnels) — see API Testing on the Sauce Labs Cloud.
Step 1 - Install Jenkins HTTP Plugin
Log in to your Jenkins account. First, click “Manage Jenkins,” then click “Manage Plugins.” We’re going to need the HTTP Request plugin. To find the plugins, click the “Available” tab in the Plugins menu and use the filter in the top right corner to search for it.

Step 2 - Generate an API Hook
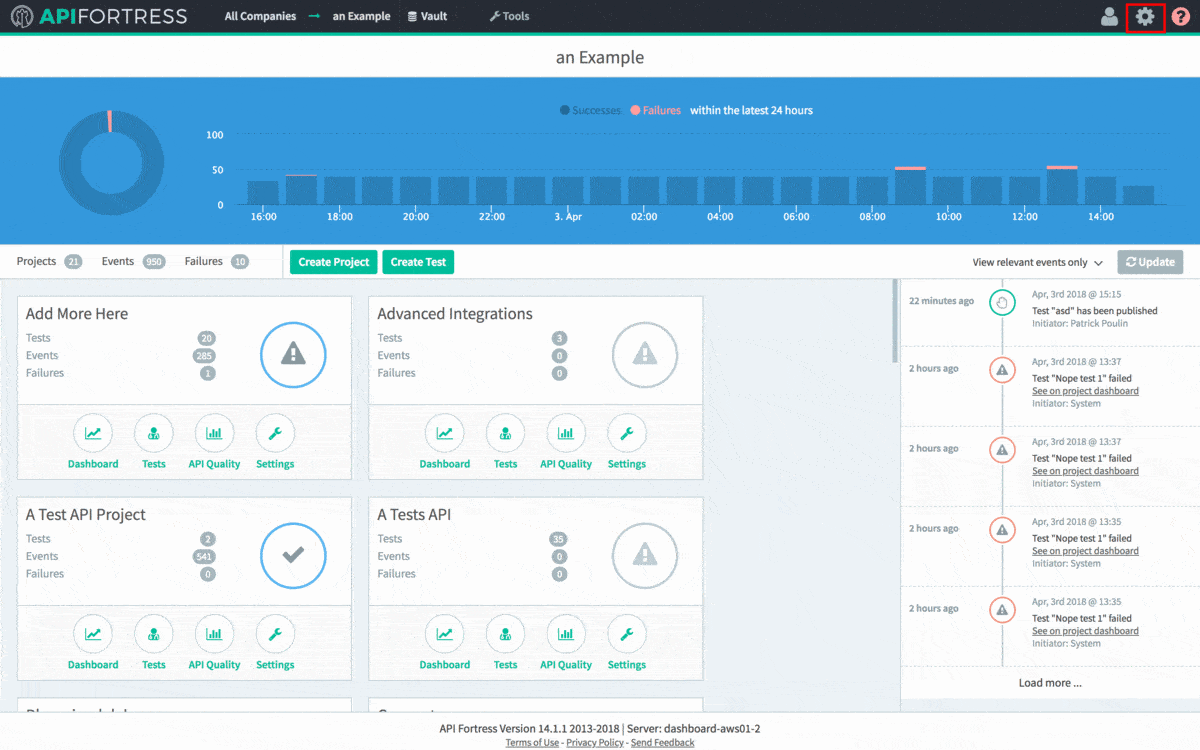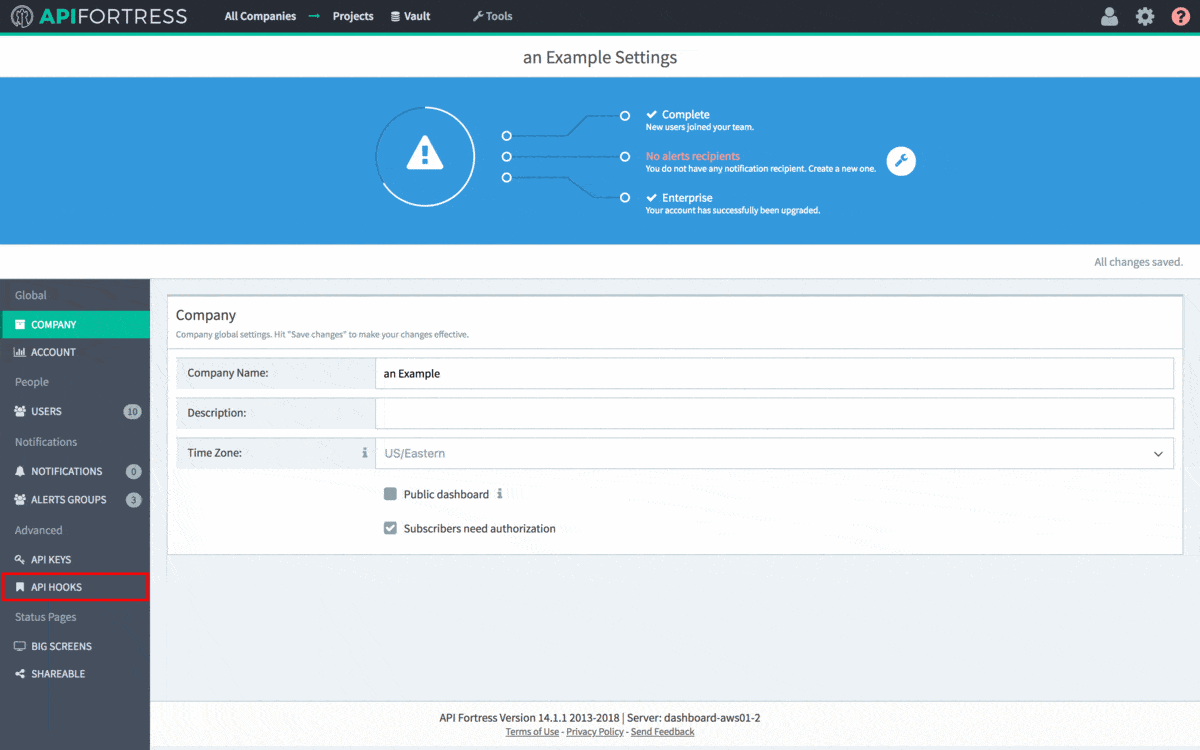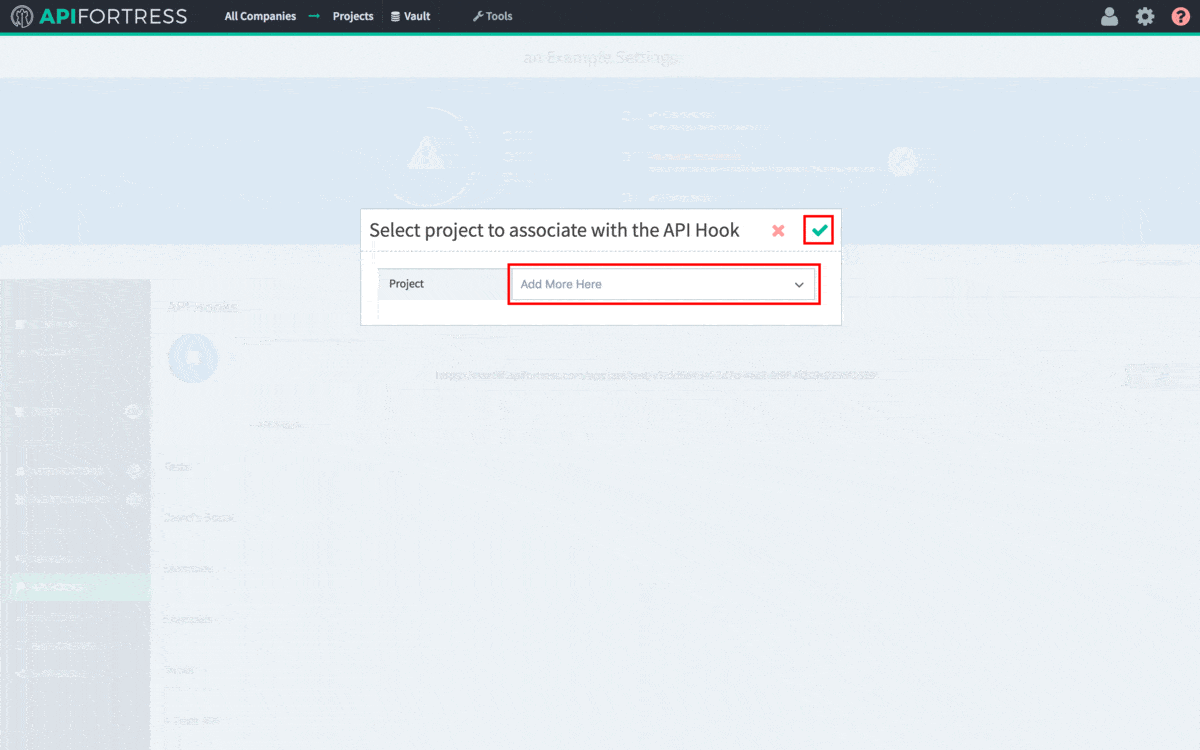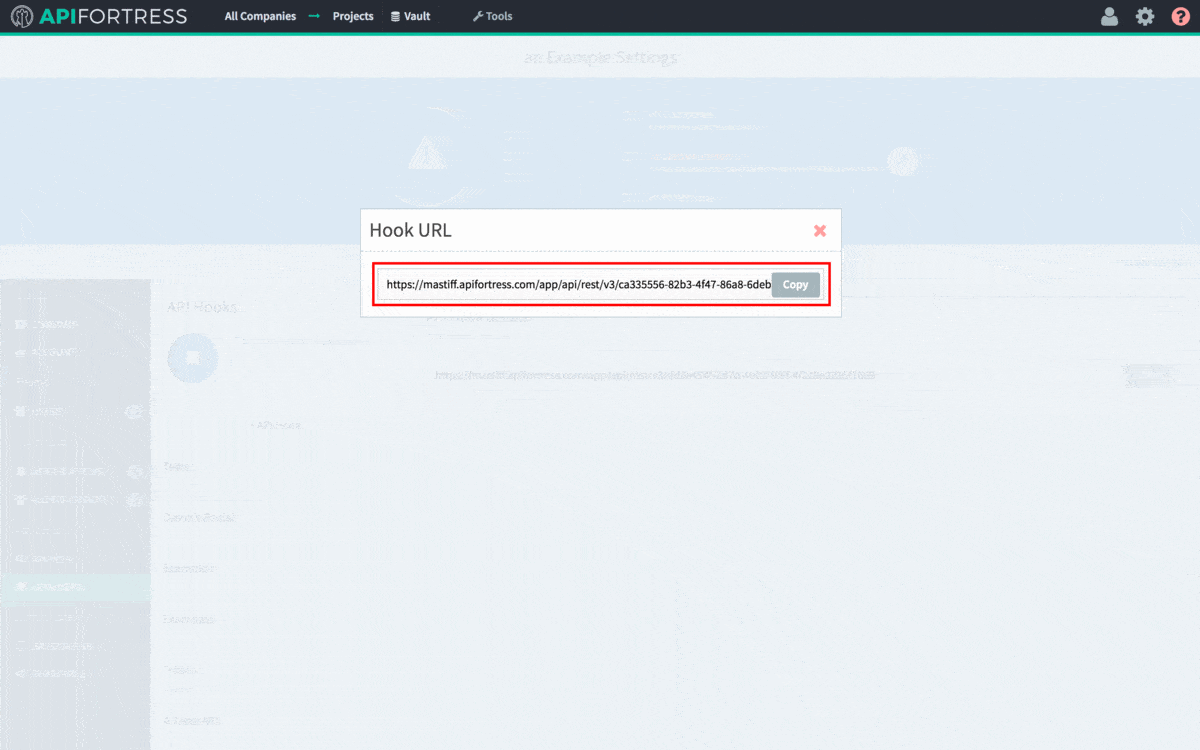
The first step to integrating API Fortress into your CI/CD process is to grab the generated API hook for the project in question. To do so, head to the Settings panel in API Fortress. This view, seen below, can be accessed from anywhere in the application by clicking the Gear icon in the top right corner of the screen. Please note you need Manager access to generate a webhook. From Settings, click the API Hooks section and generate the hook for your project.
The next step depends on what you’re trying to test. The following steps are going to assume that you wish to run all of the tests in a project. You can also run a single test, or a series of tests with a certain tag. If you would like to learn more about that please contact API Fortress.
To import our data into Jenkins as JUnit, we’ll export it in JUnit format using a query parameter. Since we already have our API hook, we just need to add the parameter to do so.
As it stands, our API hook is as follows:
https://mastiff.apifortress.com/app/api/rest/v3/86f81b19-2d29-4879-91d9-6dbb2271fec0861**
The normal command to run all of the tests in the project, per the API Fortress docs is /tests/run-all, so we append this on to the end of the API call. We also need to request JUnit output via query parameters. First, we need to set sync to true, and then we can set format to JUnit. In short, we need to append ?sync=true&format=junit. That gives us the final API call:
https://mastiff.apifortress.com/app/api/rest/v3/86f81b19-2d29-4879-91d9-6dbb2271fec0861/tests/run-all?sync=true&format=junit**
Great! If we make this API call via a browser or a tool like Postman, we can see our results in JUnit. We’re almost there.
Step 3 - Execute HTTP Call from Jenkins
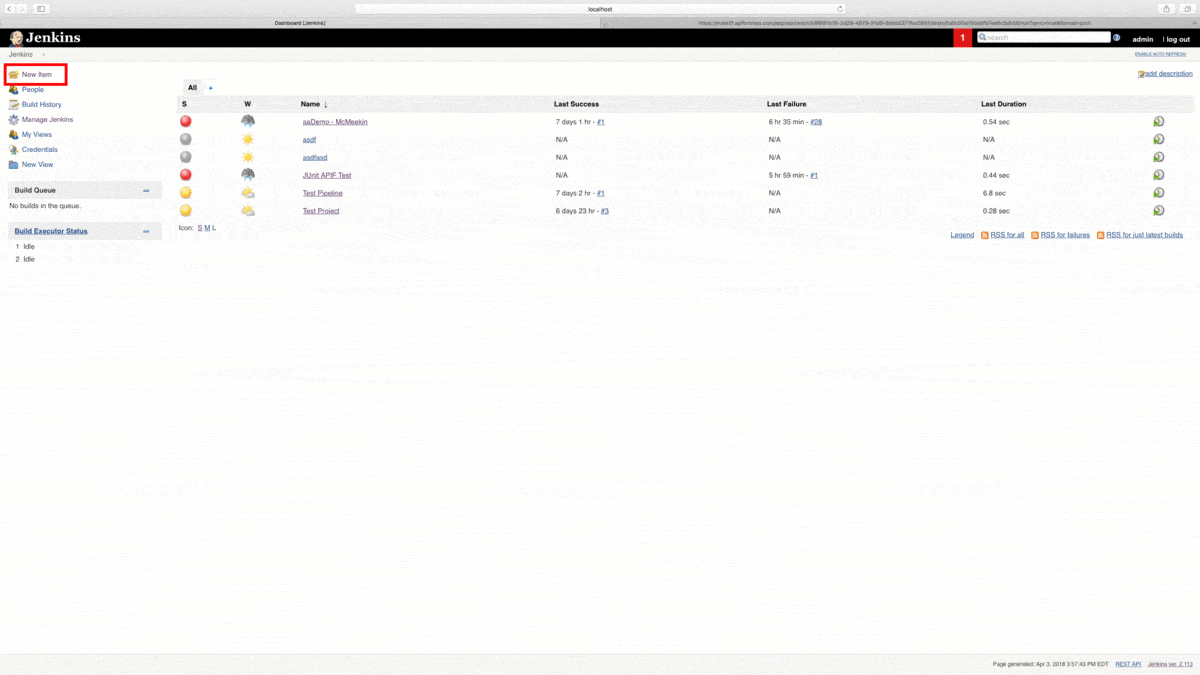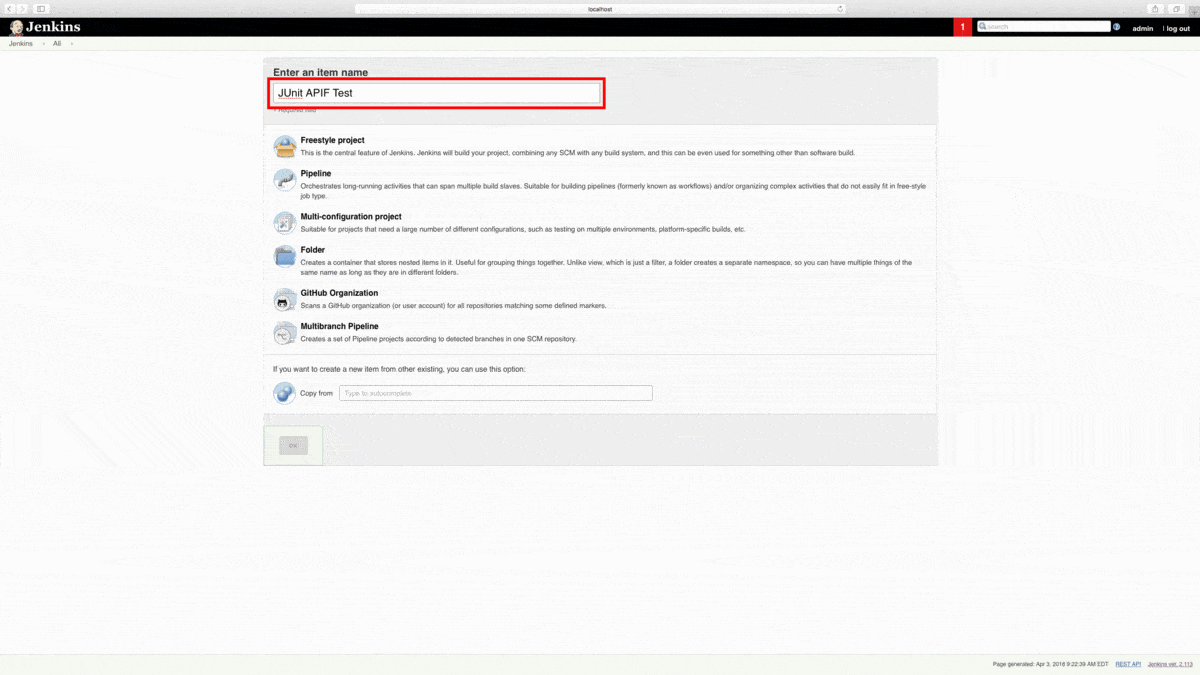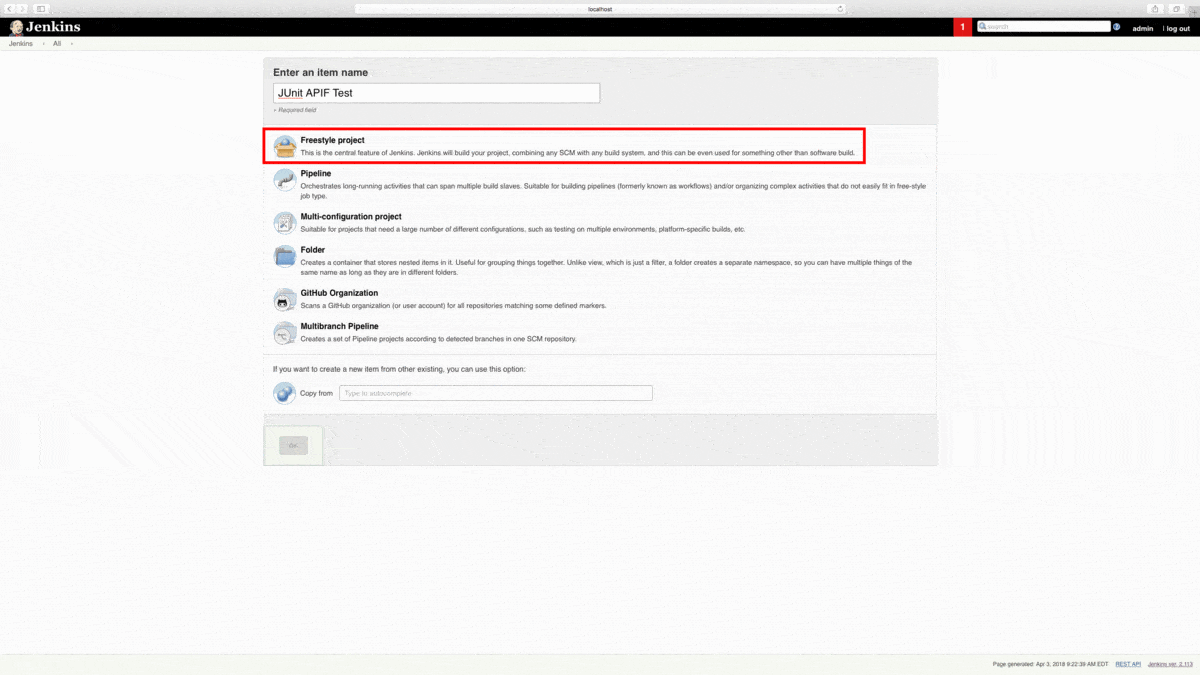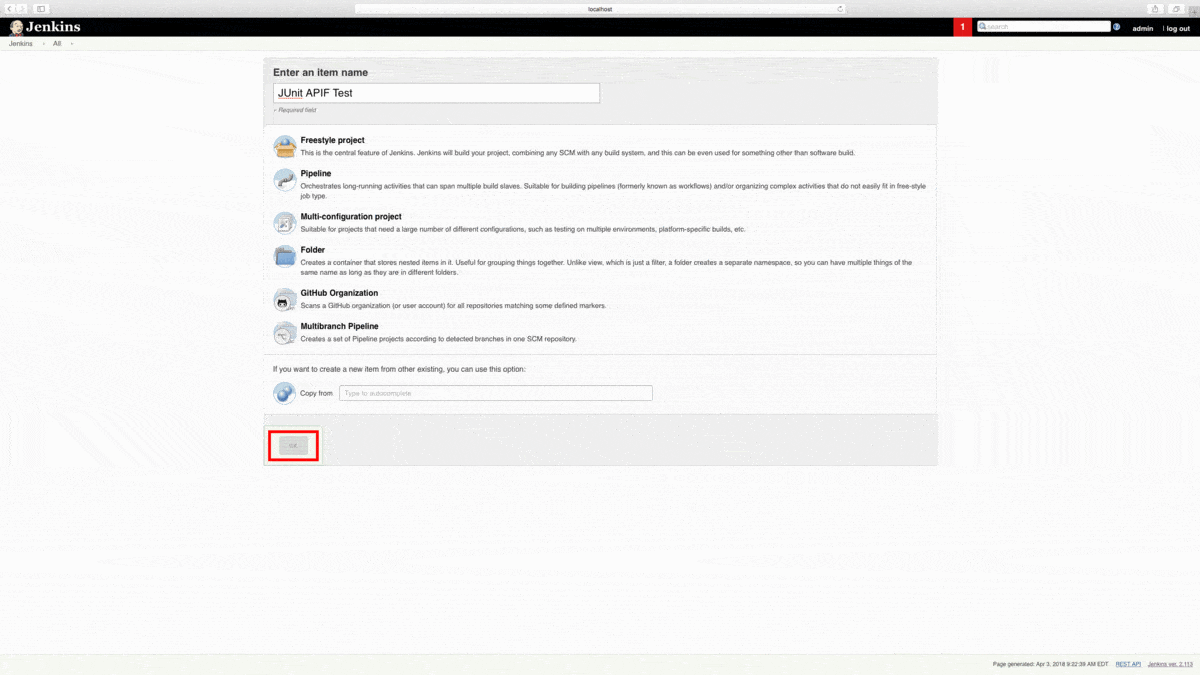
From the Jenkins dashboard, let’s create a New Item. Next, we’re going to name and create a Freestyle Project. Click the OK button to proceed.
Scroll down the page until you see the “Add Build Step” pulldown menu. Select “HTTP Request.” This option will only be available if you installed the HTTP Request plugin in the previous step. We’re going to paste the API call we created above into the URL line. If we save this configuration, we can run the build and see Jenkins receive our JUnit test results in real time. These test results can then be passed along to platforms like qTest or Zephyr in a CI/CD pipeline.